Mpox
Situation Update
Solano Public Health, along with the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) and other agencies, are monitoring a growing outbreak of mpox cases in the United States and California. There have been 17 deaths in the United States since the beginning of the outbreak; however, it does not pose a risk to the general public.
Mpox is a rare disease that is caused by infection with the mpox virus. Mpox virus is part of the same family of viruses as variola virus, the virus that causes smallpox. Mpox symptoms are similar to smallpox symptoms, but milder, and mpox is rarely fatal. Mpox is not related to chickenpox. Mpox spreads to through prolonged close, personal, often skin-to-skin contact, including sex and kissing. The virus can be spread from the time symptoms start until all sores, including scabs, have healed and a fresh layer of skin has formed. This can take several weeks.
As of 11/29/2022, there is no longer eligibility requirements. Individuals who are 18 years or older and request the JYNNEOS vaccine may get vaccinated.
CDPH Updated Guidance as of November 15, 2022: Considerations for Mpox Vaccination in California
The vaccine is being prioritized for:
- Individuals who self-attests to meeting the current eligibility criteria OR self-attests to being at risk for future exposure to Mpox
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)++ for individuals with certain risk factors who are more likely to have been recently exposed to mpox even if they have not had documented exposure to someone with confirmed mpox, such as people who attended an event or venue where there was known mpox exposure.
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)++ for individuals with certain risk factors who are more likely to have been recently exposed to mpox even if they have not had documented exposure to someone with confirmed Mpox, such as people who attended an event or venue where there was known mpox exposure.
2nd Dose of the vaccine is now available. 2nd doses will be administered to individuals who are at least 28 days from receiving their 1st dose of the JYNNEOS vaccine.
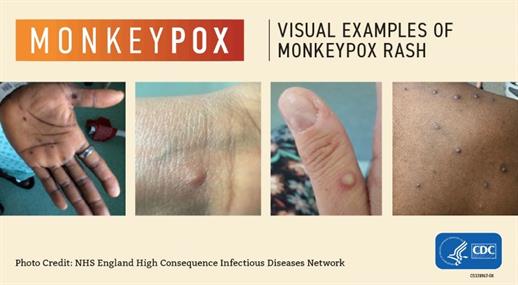
Mpox Symptoms:
Mpox symptoms usually start within two weeks of exposure to the virus. Initial symptoms are similar to flu (fever, headache, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes), followed by a rash and sores that look similar to herpes sores. The rash or sores may be located on or near the genitals or anus but could also be on other areas like the hands, feet, chest, or face.
- The sores will go through several stages, including scabs, before healing.
- The sores can look like pimples or blisters and may be painful or itchy.
- Sores may be inside the body, including the mouth, vagina, or anus.
Prevention of Mpox
There are number of ways to prevent the spread of mpox, including:
- Always talking to your sexual partner/s about any recent illness and being aware of new or unexplained sores or rashes on your body or your partner’s body, including on the genitals and anus
- Avoiding close contact, including sex, with people with symptoms like sores or rashes
- Avoid sharing the same bed or bed linens as a person with symptoms consistent with mpox
- Practicing good hand hygiene
- People who become infected should isolate until their symptoms are improving or have gone away completely. Rash should always be well covered until completely healed.
- Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) (like a mask, gown, and gloves) when caring for others with symptoms
- Avoiding contact with infected materials contaminated with the virus
- Avoiding contact with infected animals
Testing
If you have rash or spots that may look like mpox, reach out to your healthcare provider for further testing and evaluation. If you do not have a provider and are seeking to be tested, please call and schedule an appointment with a Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC). See local FQHCs below:
| Facility | Address | Phone |
| Community Medical Centers | 600 Nut Tree Rd Ste 310
Vacaville, CA | 707 359 1800 |
Community Medical Centers
Dixon Family Practice | 131 W A Street Ste 1
Dixon, CA | 707 635 1600 |
Family Health Services
Fairfield | 2201 Courage Dr
Fairfield, CA | 707 784 2010 |
Family Health Services
Vacaville | 1119 East Monte Vista Ave
Vacaville, CA | 707 469 4640 |
Family Health Services
Vallejo | 365 Tuolumne St
Vallejo, CA | 707 553 5509 |
La Clinica de la Raza
Great Beginnings | 210 Hospital Dr
Vallejo, CA | 707 645 7316 |
La Clinica de la Raza
North Vallejo | 220 Hospital Dr
Vallejo, CA | 707 641 1900 |
La Clinica de la Raza
Vallejo Medical | 415 Georgia St
Vallejo, CA | 707 556 8100 |
Until you receive guidance from your provider, you should:
- Notify people you have been in close contact with or have had sex with and ask them to get evaluated for Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP).
- Stay home and avoid close contact including sexual or intimate contact.
- Cover any blisters or skin lesions.
Isolate from others and wear a mask if you have to be around others.
Vaccine Strategies to Prevent Mpox
Interim Guidance: Intradermal Administration of JYNNEOS smallpox and Mpox Vaccine (update 08-26-2022)
Globally and in the United States, supply of the JYNNEOS vaccine remain scarce. The standard regimen for JYNNEOS involves a 2-dose subcutaneous route of administration with an injection volume of 0.5 mL, given at an interval of 28 days. In the context of the current national Public Health Emergency, an alternative regimen involving intradermal (ID) administration with an injection volume of 0.1 mL may be used under an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) issued by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Subsequent guidance from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and California Department of Public Health (CDPH), endorses the intradermal administration of JYNNEOS to maximize the number of available doses and overall risk reduction of severe Mpox.
2nd Dose of the vaccine is now available. 2nd doses will be administered to individuals who are at least 28 days from receiving their 1st dose of the JYNNEOS vaccine.
The CDC advises that people who have been exposed to Mpox be given the vaccine to prevent them from developing the disease. This is called post-exposure prophylaxis or PEP. PEP is most effective at preventing Mpox if the vaccine is administered within 4 days of exposure. If given between 4–14 days after the date of exposure, vaccination may help reduce symptoms, but may not prevent the infection from developing.
At this time, the JYNNEOS vaccine is being prioritized for the following groups:
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) for known close contacts of Mpox cases who are identified by public health via case investigation, contact tracing, and risk exposure assessments.
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)++ for individuals with certain risk factors who are more likely to have been recently exposed to Mpox even if they have not had documented exposure to someone with confirmed Mpox, such as people who attended an event or venue where there was known Mpox exposure.
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for individuals at occupational risk of Mpox according to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) guidance, including laboratory workers who perform Mpox testing
If you receive your care from the following facilities, please visit their page for more information on Mpox resources & vaccine availability.
Facility
Coadministration of JYNNEOS Vaccine with Other Vaccines
Currently, there are no data on administering JYNNEOS vaccine at the same time as other vaccines. Because JYNNEOS is based on a live, attenuated non-replicating orthopoxvirus, JYNNEOS typically may be administered without regard to timing of other vaccines. This includes simultaneous administration of JYNNEOS and other vaccines on the same day, but at different anatomic sites if possible.
However, there are additional considerations if administering a COVID-19 vaccine.
- If an orthopoxvirus vaccine is offered for prophylaxis in the setting of an orthopoxvirus (e.g., Mpox) outbreak, orthopoxvirus vaccination should not be delayed because of recent receipt of a Moderna, Novavax, or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine; no minimum interval between COVID-19 vaccination with these vaccines and orthopoxvirus vaccination is necessary.
- People, particularly adolescent or young adult males, might consider waiting 4 weeks after orthopoxvirus vaccination (either JYNNEOS or ACAM2000) before receiving a Moderna, Novavax, or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, because of the observed risk for myocarditis and/or pericarditis after receipt of ACAM2000 orthopoxvirus vaccine and mRNA (i.e., Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech) and Novavax COVID-19 vaccines and the unknown risk for myocarditis and/or pericarditis after JYNNEOS.
Timing of Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) or an Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) in relation to JYNNEOS Vaccine
Timing of TB Testing (TST or IGRA) should be delayed by four (4) weeks post JYNNEOS vaccine.
Standing Orders for Standard (subcutaneous) & Alternative (intradermal) Jynneos Vaccination (from CDC)
Adults in General Population | JYNNEOS Smallpox and Mpox Vaccine | Standing Orders for Administering Vaccine Intradermally: Alternative Dosing Regimen
Adults with Certain Medical Conditions | JYNNEOS Smallpox and Mpox Vaccine | Standing Orders for Administering Vaccine Subcutaneously: Standard Regimen
Requesting Vaccine Allocations (Hospital and Clinic Systems Only)
Requests for initial and additional doses of Jynneos vaccine should be made via the MHOAC by calling (707) 784-8155 during regular business hours or email [email protected].
Mpox-Specific Health Alerts for Providers:
Jynneos Vaccine Accountability Form
As of Monday, August 1st, the CDC no longer requires submission of this form and is discontinued.
Resources
Press Release: Solano Public Health confirms case of Mpox
CDC Mpox Updates | Mpox: Get the Facts Sheet
CDPH Mpox Q&A | Mpox case count in California | Communications Toolkit | Mpox Menu of Resources | Mpox Home Isolation Guidance for the General Public
Governor Newsom Declares State of Emergency for Mpox
Solano Public Health Mpox Townhall
Mpox Townhall Recording
Mpox Townhall PPT Slides.